Random walker segmentation¶
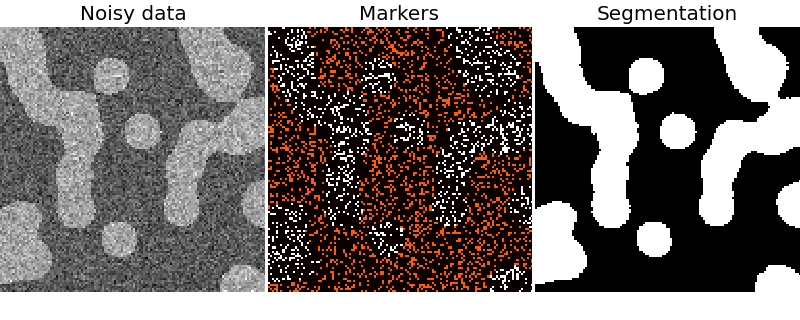
The random walker algorithm [1] determines the segmentation of an image from a set of markers labeling several phases (2 or more). An anisotropic diffusion equation is solved with tracers initiated at the markers’ position. The local diffusivity coefficient is greater if neighboring pixels have similar values, so that diffusion is difficult across high gradients. The label of each unknown pixel is attributed to the label of the known marker that has the highest probability to be reached first during this diffusion process.
In this example, two phases are clearly visible, but the data are too noisy to perform the segmentation from the histogram only. We determine markers of the two phases from the extreme tails of the histogram of gray values, and use the random walker for the segmentation.
| [1] | Random walks for image segmentation, Leo Grady, IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006 Nov; 28(11):1768-83 |
print __doc__
import numpy as np
from scipy import ndimage
from skimage.segmentation import random_walker
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def microstructure(l=256):
"""
Synthetic binary data: binary microstructure with blobs.
Parameters
----------
l: int, optional
linear size of the returned image
"""
n = 5
x, y = np.ogrid[0:l, 0:l]
mask = np.zeros((l, l))
generator = np.random.RandomState(1)
points = l * generator.rand(2, n ** 2)
mask[(points[0]).astype(np.int), (points[1]).astype(np.int)] = 1
mask = ndimage.gaussian_filter(mask, sigma=l / (4. * n))
return (mask > mask.mean()).astype(np.float)
# Generate noisy synthetic data
data = microstructure(l=128)
data += 0.35 * np.random.randn(*data.shape)
markers = np.zeros(data.shape, dtype=np.uint)
markers[data < -0.3] = 1
markers[data > 1.3] = 2
# Run random walker algorithm
labels = random_walker(data, markers, beta=10, mode='bf')
# Plot results
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3.2))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.imshow(data, cmap='gray', interpolation='nearest')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('Noisy data')
plt.subplot(132)
plt.imshow(markers, cmap='hot', interpolation='nearest')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('Markers')
plt.subplot(133)
plt.imshow(labels, cmap='gray', interpolation='nearest')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('Segmentation')
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.01, wspace=0.01, top=1, bottom=0, left=0,
right=1)
plt.show()
Python source code: download (generated using mpltools 0.6dev)
